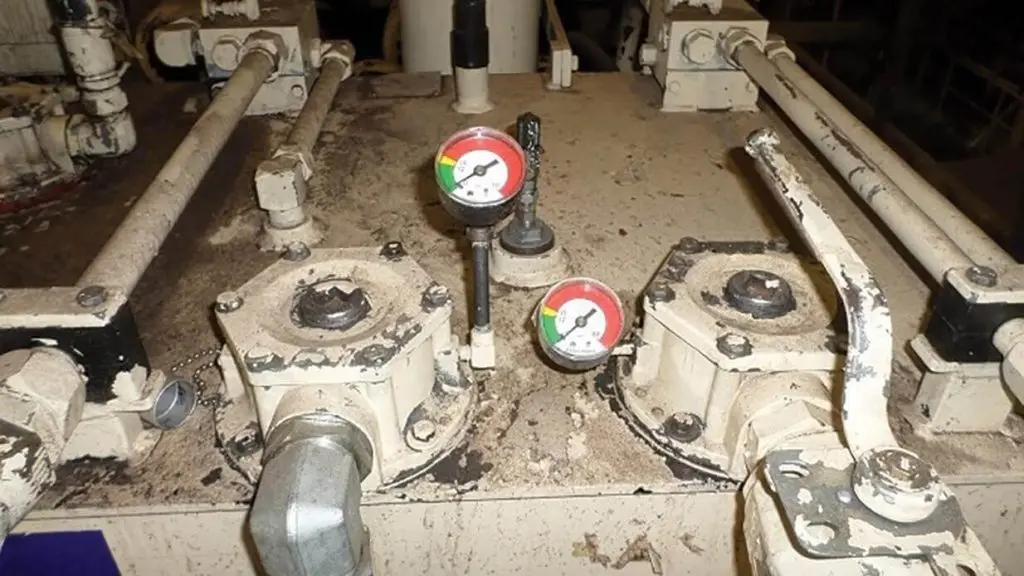
Hydraulic systems are the backbone of countless industrial and agricultural machines. They are responsible for operating heavy equipment, agricultural machinery, and construction vehicles. At the back end, these systems rely on hydraulic pumps to generate the pressurized fluid that powers their movements.
So, when hydraulic pumps malfunction, the consequences can range from reduced performance to complete system failure.
This is why it is better to stay informed about the most common hydraulic pump problems and troubleshooting techniques.
In this article, we’ll provide a step-by-step guide to identifying and troubleshooting hydraulic pump problems. Additionally, we’ll share some workable maintenance tips and preventive measures to prolong the lifespan of your hydraulic system.
Let’s first start with symptoms.
Common Symptoms of Hydraulic Pump Problems
Identifying hydraulic pump issues is the first step in addressing potential problems and preventing costly downtime. And rightly so—you can’t fix what you don’t know is broken.
In the lines below, we have outlined some symptoms that you could look at if there is a problem with your hydraulic pump.
Fluid Leakage
Hydraulic fluid leaks are often the first visible sign of a hydraulic pump problem. Leaks can occur at various points in the system, including seals, hoses, and fittings. While minor leaks may not immediately impact performance, they should not be ignored. If ignored for long, they can lead to significant fluid loss, reduced system efficiency, and potential environmental hazards.
Unusual Noises
Hydraulic pumps typically operate quietly and smoothly. However, when problems arise, they may start producing unusual noises, such as whining, screeching, or knocking sounds. Various factors, including worn bearings, damaged gears, or cavitation, can cause these noises.
Decreased Performance
A noticeable decline in performance is another common symptom of hydraulic pump problems. This can manifest in various ways, such as slower actuator movement, reduced lifting capacity, or erratic system operation.
If you notice a drop in performance, investigate the underlying cause, as it could indicate a failing hydraulic pump.
Overheating
Hydraulic pumps generate heat during operation, but excessive heat can indicate a problem. If the pump becomes abnormally hot to the touch, it could indicate internal wear, cavitation, or contamination in the hydraulic fluid.
Erratic Movement
Erratic movement of hydraulic actuators is another symptom that should not be overlooked. This can manifest as jerky, unstable movement or a reluctance to respond to control inputs. Such erratic behavior can be caused by various factors, including a failing pump, clogged valves, or air in the system.
These are some of the symptoms. While you can troubleshoot some problems, others may require the assistance of an expert.
In any case, it is better to know about how to fix your hydraulic pump problems.

Hydraulic Pump Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Now that we have a bit of knowledge about common hydraulic pump symptoms, let’s talk about the practical aspects of troubleshooting and rectifying prevalent hydraulic pump problems.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of common issues and their corresponding troubleshooting steps:
Step 1: Check Fluid Level and Condition
First of all, check the fluid level and condition. Hydraulic fluid plays a key role in the operation and lubrication of the pump. Check the fluid level in the reservoir and ensure it meets the manufacturer’s specifications. Inspect the fluid for any signs of contamination, such as discoloration, debris, or excessive foaming.
You must change the fluid and replace the filter if any contamination is present.
Step 2: Address Cavitation Issues
Cavitation occurs when the pressure at the pump’s intake drops below the vapor pressure of the fluid, causing bubbles to form. These bubbles collapse violently, leading to noise, vibration, and reduced performance.
Troubleshooting Techniques and Solutions
- Check for leaks: Tighten loose connections, if any, and replace damaged hoses or fittings. Leaks can allow air to enter the system, lowering the intake pressure and triggering cavitation.
- Ensure proper fluid level and viscosity: Maintain the correct fluid level and use the recommended fluid viscosity for your pump. Low fluid levels or improper viscosity can contribute to cavitation.
- Reduce pump speed: Adjust the pump speed to match the system requirements and avoid excessive pressure drops. Operating the pump at a higher speed than necessary can exacerbate cavitation issues.
Step 3: Fix Overheating Issues
Internal wear, cavitation, or contamination can cause excessive heat generation in the hydraulic pump. Overheating can damage pump components and lead to premature failure.
Troubleshooting Techniques and Solutions
- Check for wear: Inspect the pump for worn bearings, gears, or seals and replace them if necessary. Worn components can generate excessive friction, leading to overheating.
- Address cavitation issues: Follow the cavitation troubleshooting techniques mentioned above to eliminate cavitation, which can also contribute to overheating.
- Perform fluid changes and filter replacements: Change the hydraulic fluid and replace filters regularly to maintain cleanliness. Contaminated fluid can restrict heat dissipation and cause overheating.
Step 4: Troubleshooting Contamination Issues
Contaminants in the hydraulic fluid, such as dirt, debris, or metal particles, can damage pump components, impede performance, and accelerate wear.
Troubleshooting Techniques and Solutions
- Check for leaks: Identify and seal any leaks that could allow contaminants into the system. Leaks provide an entry point for dirt, debris, or moisture.
- Replace filters regularly: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended filter replacement schedule to remove contaminants from the fluid. Filters trap impurities and prevent them from harming pump components.
- Replace fluid: If the fluid is contaminated, you have no option but to replace it.
Step 5: Fixing Erratic Movement
The erratic movement of hydraulic actuators, characterized by jerky, unstable movement or a reluctance to respond to control inputs, can indicate various issues.
Troubleshooting Techniques and Solutions:
- Check for air in the system: Bleed air from the hydraulic system using the manufacturer’s recommended procedures. Air in the system can interfere with fluid flow and cause erratic movement.
- Inspect valves and seals: Check for worn, damaged, or sticking valves and seals and replace them if necessary. Faulty valves can disrupt fluid flow, leading to erratic movement.
- Verify proper control system operation: Ensure the control system is functioning correctly and sending the right signals to the pump and actuators. Faulty control signals can cause erratic movement.
As mentioned earlier, some of the issues discussed above are better fixed by a qualified hydraulic technician. However, there are a few things discussed below that you can do to make sure that your system is working smoothly and efficiently.

Maintenance and Preventive Tips
Preventive maintenance is the cornerstone of a reliable and long-lasting hydraulic system. With proper care and maintenance, you can prevent many minor hydraulic pump problems from becoming bigger problems.
How? Here are some practical tips.
Regular Fluid Checks
Hydraulic fluid is the lifeblood of a hydraulic system, providing lubrication, power transmission, and heat dissipation. Regular fluid checks are essential to maintain optimal system performance. Check the fluid level regularly and ensure it meets the manufacturer’s specifications. If you see any problem with the fluid, change it right away.
Timely Filter Replacements
Filters are responsible for removing contaminants from the hydraulic fluid and protecting the pump and other components from wear and damage. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended filter replacement schedule and consider increasing the frequency if the system operates in a dusty or dirty environment.
Routine Inspections
At the same time, do not forget regular inspections of the pump and its surroundings. Look for signs of fluid leaks, cracks, or damage to hoses, fittings, and the pump housing. Check for excessive wear on visible components and ensure all connections are secure. If there are any signs of wear or damage, address them promptly to prevent potential escalation into complex hydraulic pump problems.
Proper Fluid Selection
Some systems, especially older ones, may require more viscous fluid than the newer ones. Improper fluid selection can lead to premature wear, cavitation, and reduced system efficiency. So, always consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or your hydraulic technician for the appropriate fluid type and viscosity.
Proper Storage
When not in use, properly store hydraulic pumps and machinery to prevent potential damage and contamination. Before storage, drain the fluid if the equipment will be out of service for an extended period. Cover the pump and its surroundings to prevent dust and moisture ingress. Make sure that all the exposed components are protected.
Broken Hydraulic Pump? There’s Always a Replacement
If your hydraulic pump has reached the end of its lifespan or has suffered irreparable damage, go to a trusted brand like VEVOR for an efficient and durable hydraulic pump.
At VEVOR, we offer a comprehensive selection of hydraulic pumps to meet the diverse requirements of various industries and applications. Our extensive catalog includes a wide range of pump types, including gear pumps, PTO pumps, and electric-driven hydraulic pumps, catering to a variety of flow rates, pressures, and power requirements.

Consider your needs, explore our collection, and choose the pump that best meets your requirements.
Conclusion
Malfunctioning of hydraulic pumps can lead to a significant downturn in the performance of the hydraulic-powered machinery, and in certain cases, it may even halt the operations altogether. Therefore, you must always keep an eye out for common symptoms of hydraulic pump problems. If you detect any issue, you should address it promptly by following the hydraulic pump troubleshooting steps discussed above and referring to the user manual.
With proper maintenance and early detection and intervention, you can save time, money, and potential safety hazards and ensure that your hydraulic pump keeps working seamlessly for many years to come.
If your hydraulic pump is beyond repair, consider replacing it with an efficient and durable pump from VEVOR—a brand known for top quality!