Linear actuators are all around us—in machines, tools, and systems that need precise, straight-line movement. From opening valves to lifting heavy parts, they make things move smoothly and accurately. There are many types to choose from, including electric linear actuators, servo linear actuators, as well as hydraulic, pneumatic, and piezoelectric options.
Each one works a little differently, but all serve the same purpose: turning energy into motion. Knowing the types of linear actuators helps you pick the right one for your task. Whether it’s a small task or a heavy-duty job, this blog will help you find the right actuator to get it done with precision.
Understanding the Different Types of Linear Actuators
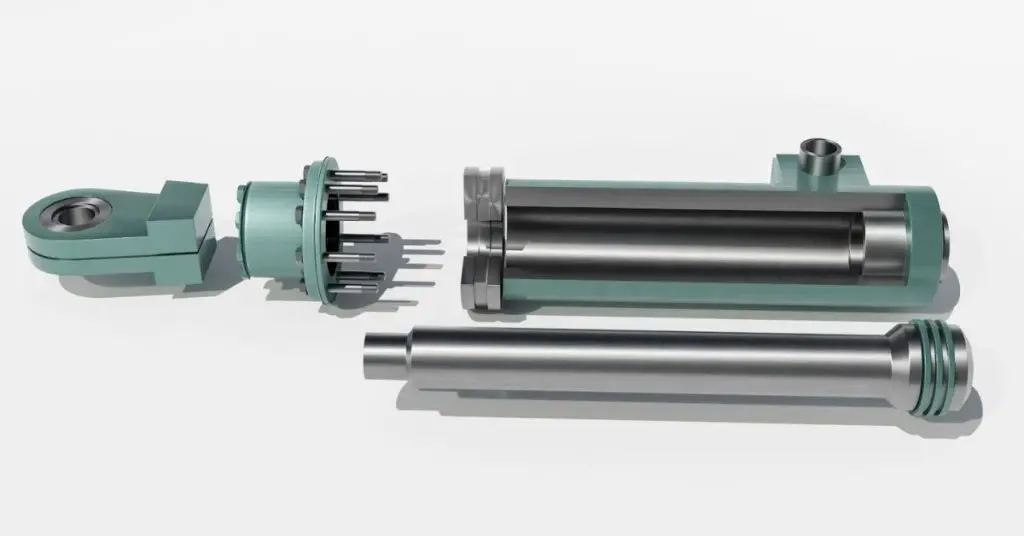
A linear actuator moves objects in a straight line, making it ideal for machines that need precise push, pull, or lift motions. You’ll see these in robotics, factory systems, hospital beds, and more. They allow parts to move exactly where needed, often with just the push of a button or a simple control system.
There are several types of linear actuators, each designed for a specific job and environment. Some use electricity, while others rely on air or fluid pressure. Knowing the options helps you figure out how to choose the right linear actuator for your task.
Here are the main types:
- Electric linear actuators – use electric motors for clean, controlled motion
- Servo linear actuators – offer high precision and programmable movement
- Hydraulic linear actuators – ideal for heavy loads and rugged environments
- Pneumatic linear actuators – fast and lightweight, using compressed air
- Piezoelectric actuators – provide tiny, ultra-precise motion for scientific and medical equipment
By learning about the types of linear actuators and their applications, you’ll be better equipped to match the right kind to your automation or mechanical needs.
Electric Linear Actuators
Electric linear actuators change electrical energy into straight-line motion using a motor and a screw, belt, or gear system. Electric linear actuator types, like screw-driven and belt-driven models, are used in robotics, smart homes, and manufacturing. Screw-driven types are great for precise tasks, while belt-driven ones are better for fast movement.
These actuators are quiet, low-maintenance, and work best in clean spaces. Some versions, like DC actuators and rack-and-pinion systems, serve vehicles and gear-based needs. If you’re wondering about the best type of linear actuator for automation, electric actuators are often the top pick for accuracy and control.
Servo Linear Actuators
Servo linear actuators are a specialized kind of electric actuator. They include a servo motor that allows for exact control over position, speed, and force. These actuators are ideal for use in CNC machines, robotics, and smart factory systems where every move must be accurate.
Servo actuators often come with built-in sensors, helping them detect position and adjust in real time. This makes them perfect for repetitive, high-precision tasks. If you’re searching for the best type of linear actuator for automation, servo options deliver superior performance in complex operations.
Hydraulic Linear Actuators
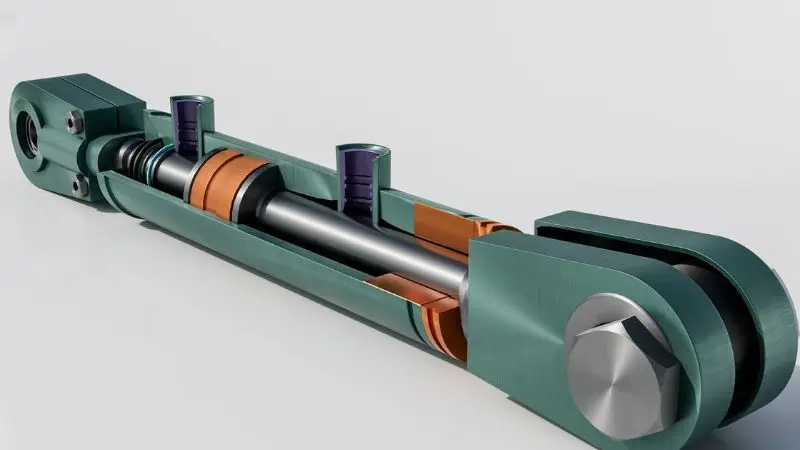
Hydraulic linear actuators use pressurized liquid to create movement. These actuators are designed for heavy-duty tasks and are commonly found in construction equipment and industrial presses. They provide a strong force and can operate in harsh or dirty environments. While powerful, they do require regular maintenance and come with the added components of pumps, hoses, and fluid reservoirs.
Still, in terms of strength and durability, they are unmatched in heavy applications. When thinking about how to choose the right linear actuator, consider hydraulic versions if your project demands large-scale force and rugged performance.
Pneumatic Linear Actuators
Pneumatic actuators rely on compressed air to produce straight movement. They are widely used in packaging lines, food processing, and assembly tasks where speed is more important than accuracy. These actuators are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to maintain.
You might also come across vacuum-based versions, which use negative pressure instead of air compression. These are perfect for cleanroom environments or handling delicate items. Types of linear actuators and their applications include pneumatic ones in high-speed, low-complexity jobs where simplicity and safety matter.
Piezoelectric Actuators
Piezoelectric actuators are designed for extremely precise, tiny movements. They use special materials that slightly expand when electricity is added, making them ideal for tasks that require nanometer-level accuracy. These actuators are most often found in scientific tools like microscopes and optical equipment.
They perform best in clean, controlled environments and are trusted in research and high-tech fields. While not as common as other electric linear actuator types, they’re essential for ultra-fine motion control. If your work involves delicate adjustments, piezoelectric actuators are a smart choice to consider in your set of linear motion tools.
Comparing the Main Types of Linear Actuators
When deciding between actuator options, you need to look closely at force, speed, precision, and environment. Each of the types of linear actuators and their applications brings something different to the table. The right choice depends on your project’s specific needs.
Comparing Force and Load Capacity
The first step in how to choose the right linear actuator is knowing how much weight it needs to move. This is called load capacity. Some actuators are made for heavy-duty lifting, while others are designed for lighter, more delicate work.
- Hydraulic linear actuators offer maximum force, making them ideal for lifting heavy machinery and moving large industrial parts with ease.
- Electric actuators handle medium loads well, delivering steady, energy-efficient performance in automation systems that require precision and reliability.
- Servo linear actuators offer strong force plus detailed control. Choose them when you need strength and programmable motion.
- Pneumatic actuators are ideal for light-duty tasks, offering quick, simple motion but lacking the power needed for heavy-duty lifting applications.
- Piezoelectric actuators handle tiny loads with extreme accuracy. They’re ideal for lab instruments and delicate movements.
When power is your priority, go with hydraulic actuators. For smaller tasks, electric linear actuator types or pneumatic options are often a better fit.
Speed and Precision in Motion
Next, think about how fast your actuator needs to move and how accurate it must be. Some types shine in speed, while others are built for detailed control.
- Electric actuators offer good speed and excellent accuracy. They’re widely used in tasks that demand consistent positioning.
- Servo linear actuators provide top-level motion control. They’re programmable and ideal for repetitive or exact movements.
- Pneumatic actuators are extremely fast but not highly precise. They work best in basic, quick-moving operations.
- Hydraulic actuators move slowly but deliver constant pressure. Choose them when you care more about force than speed.
- Piezoelectric actuators are unmatched in fine precision. They’re built for microscopic tasks in labs or clean rooms.
If your project requires high-speed precision, servo linear actuators or piezoelectric actuators are the best options.
Choosing Based on Environment
Where your actuator will operate plays a big role in the type you should select. Some are built to handle messy conditions, while others require clean surroundings.
- Hydraulic actuators perform reliably in tough outdoor conditions, handling dirt, heat, and moisture with high durability.
- Electric actuators operate best in clean, dry indoor environments, often found inside enclosed or climate-controlled systems.
- Servo actuators require stable, controlled settings and are commonly used in labs, robotics, and precision manufacturing facilities.
- Pneumatic actuators can handle a variety of conditions, including dusty or damp areas, making them great for food packaging or assembly lines.
- Piezoelectric actuators need extremely clean environments to function properly. They’re perfect for medical tools or optics.
So, if your workspace is rugged or exposed to moisture, avoid electric types. For lab or medical applications, electric linear actuator types and piezo models are often ideal.
Real-World Applications of Different Linear Actuator Types

Understanding the types of linear actuators and their applications is key to making the right choice for your project. Each actuator type is designed for specific environments, force needs, and motion control. Let’s look at where and how each one is best used.
- Electric linear actuators are great for automated systems in smart homes, manufacturing lines, and robotic arms. They offer reliable motion, easy control, and energy efficiency, making them a top choice for everyday automation tasks.
- Servo linear actuators are commonly found in CNC machines, advanced robotics, and lab equipment. They provide high-speed, precise movement and are the best type of linear actuator for automation that requires feedback control and accuracy.
- Hydraulic actuators shine in industries that demand raw power, like construction, material handling, and industrial presses. They’re ideal for heavy lifting and environments where strength is more important than speed or fine control.
- Pneumatic actuators are used in food packaging, assembly lines, and other fast-moving production systems. They’re great when you need quick, repeated movement in a clean or semi-clean environment.
- Piezoelectric actuators handle ultra-precise tasks, such as positioning microscope lenses, adjusting optical components, or controlling surgical instruments. These actuators are essential in medical, scientific, and micro-engineering fields.
Choosing the right actuator becomes easier when you fully understand each one’s strengths. Whether you’re optimizing a factory line or fine-tuning lab equipment, the right fit depends on your environment, precision needs, and motion control goals.
Wrap Up
Choosing the right linear actuator depends on what your job needs—whether it’s high force, fast movement, or exact control. From electric linear actuator types to servo, hydraulic, pneumatic, and piezoelectric, each one has a purpose. When you understand the types of linear actuators and their applications, it becomes easier to make the right decision.
Whether you’re building machines, upgrading automation, or working in labs, there’s an actuator that fits. Always consider where it will be used and what kind of movement you need. With this knowledge, you’ll know how to choose the right linear actuator for any task.
FAQ
What is the main difference between electric and hydraulic linear actuators?
Electric actuators use motors and electricity to make things move. Hydraulic actuators use liquid that is pushed under pressure. Hydraulic actuators can give you more force. Electric actuators let you control movement better. They work best in clean places.
Can you use linear actuators outdoors?
You can use hydraulic and pneumatic actuators outside. They can handle dirt, water, and bad weather. Electric and piezoelectric actuators are better for inside. They need clean and dry spaces.
How do you choose the right linear actuator for your project?
Tip: Make a list of what you need, like force, speed, and precision. Think about where you will use the actuator. Pick the type that matches your needs. If you are not sure, ask a supplier for help.
Do linear actuators need a lot of maintenance?
Most electric and piezoelectric actuators do not need much care. Hydraulic actuators need to be checked often for leaks. Pneumatic actuators need clean air and some care. Always follow the maker’s instructions.